2010-future
Global Health Impact Programs
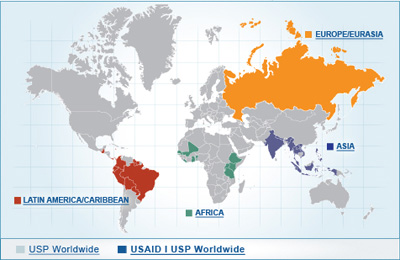
USP's global health initiatives aim to provide USP's standards to underserved countries through grants and philanthropic funding. The initiatives include PQM, the Technical Assistance Program (TAP), the Center for Pharmaceutical Advancement and Training (CePAT) in Accra, Ghana, and laboratory networks that support Official Medicines Control Laboratories (OMCLs) in three regions (Latin America, Middle East/North Africa, and Africa). These initiatives are designed to build capacity and also strengthen regulatory agencies and their quality control laboratories. Recently, USP joined the Clinton Global Initiative, expanding its work in the area of global public health with a focus on substandard, falsified, and counterfeit medicines.
In 2011, USP/PQM registered in Ethiopia as a nongovernmental organization. PQM also launched Medicines Quality Database (MQDB), a public database of medicines that is collected and analyzed in collaboration with stakeholders from countries in Africa, South America, and Southeast Asia.
In February 2011, USP launched a TAP pilot to provide developing countries with tools and training to increase their capacity to test the quality of medicines provided for their citizens.
CePAT is scheduled to open in 2013 in Accra, Ghana, and will serve all of Sub-Saharan Africa.